Why Hard Science and Medicine Is Getting Mushy

Arthur Caplan, one of America’s top medical ethicists, is worried about pollution. Not the kind that ruins our oceans or makes it hard for us to breathe, but the kind that poses a threat to the “trustworthiness, utility, and value of science and medicine.”
Caplan, who directs the Division of Medical Ethics at NYU Langone Medical Center, wrote a blistering essay in last week’s Mayo Clinic Proceedings, saying, "The pollution of science and medicine by plagiarism, fraud, and predatory publishing is corroding the reliability of research. Yet neither the leadership nor those who rely on the truth of science and medicine are sounding the alarm loudly or moving to fix the problem with appropriate energy."
He goes on to cite three causes of publication pollution, which can undermine these areas of “hard science” that should be sacrosanct.
- The proliferation of journals that recruit authors who pay to get their articles published. Despite having substandard or no peer view, these "predatory publishers" now comprise an estimated 25 percent of all open-access journals. "Not only do they provide opportunities for the unscrupulous in academia and industry to pad their curriculum vitaes and bibliographies with bogus articles and editorial appointments, they also make it difficult for those involved in the assessment and promotion of scholars to discern value from junk," writes Dr. Caplan.
- Research misconduct, like falsifying or fabricating data or concealing serious violations. Fourteen percent of scientists report that their colleagues falsify data, and 72 percent report other questionable practices, according to one 2009 study published in PLoS One.
- Plagiarism, which, according to a 2010 Nature article was "staggering," requiring editors to spend "inordinate amounts of time" checking submissions they receive.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Biggest Outrage in Atlanta’s Crazy Teacher Cheating Case
- $45 Billion in Tax Dollars Goes Missing in Afghanistan
- How Dark Money Is Distorting Politics and Undermining Democracy
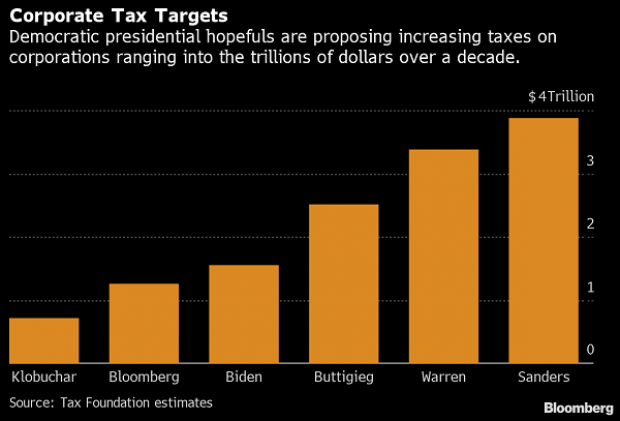
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
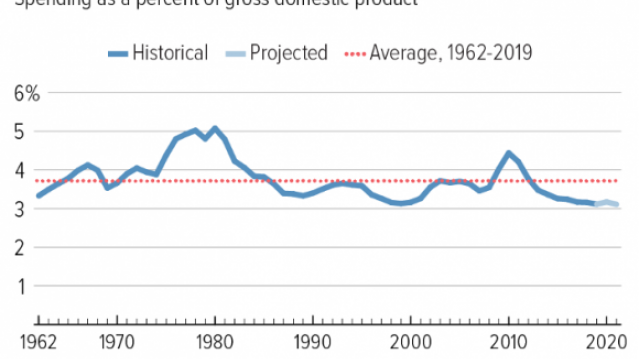
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
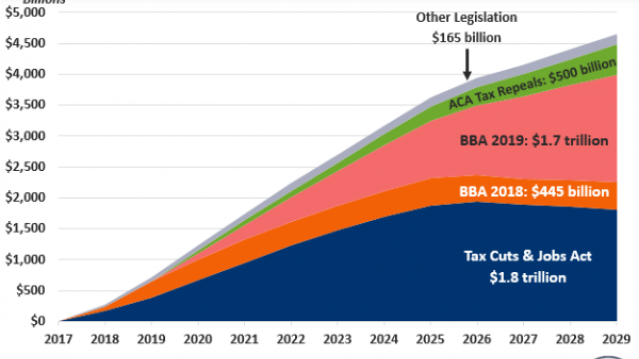
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
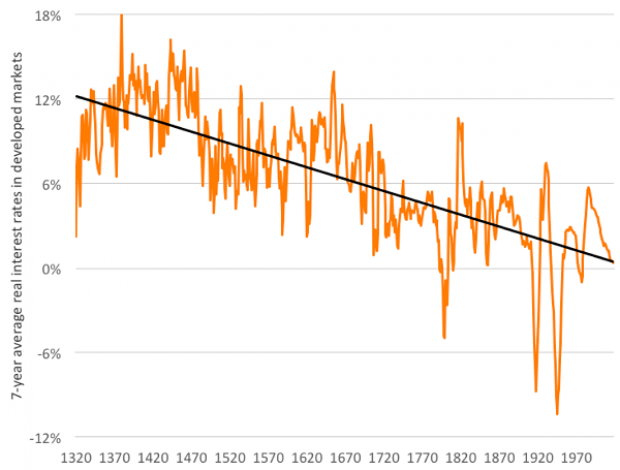
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
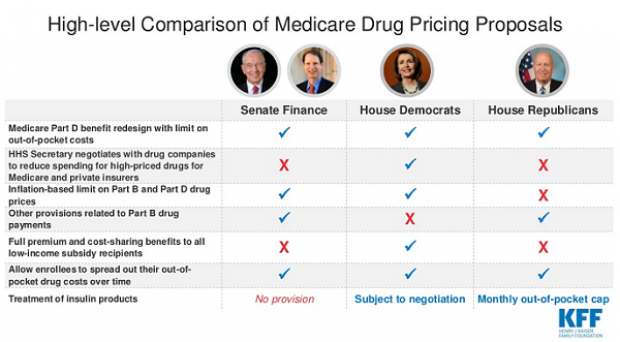
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.