Why Hard Science and Medicine Is Getting Mushy

Arthur Caplan, one of America’s top medical ethicists, is worried about pollution. Not the kind that ruins our oceans or makes it hard for us to breathe, but the kind that poses a threat to the “trustworthiness, utility, and value of science and medicine.”
Caplan, who directs the Division of Medical Ethics at NYU Langone Medical Center, wrote a blistering essay in last week’s Mayo Clinic Proceedings, saying, "The pollution of science and medicine by plagiarism, fraud, and predatory publishing is corroding the reliability of research. Yet neither the leadership nor those who rely on the truth of science and medicine are sounding the alarm loudly or moving to fix the problem with appropriate energy."
He goes on to cite three causes of publication pollution, which can undermine these areas of “hard science” that should be sacrosanct.
- The proliferation of journals that recruit authors who pay to get their articles published. Despite having substandard or no peer view, these "predatory publishers" now comprise an estimated 25 percent of all open-access journals. "Not only do they provide opportunities for the unscrupulous in academia and industry to pad their curriculum vitaes and bibliographies with bogus articles and editorial appointments, they also make it difficult for those involved in the assessment and promotion of scholars to discern value from junk," writes Dr. Caplan.
- Research misconduct, like falsifying or fabricating data or concealing serious violations. Fourteen percent of scientists report that their colleagues falsify data, and 72 percent report other questionable practices, according to one 2009 study published in PLoS One.
- Plagiarism, which, according to a 2010 Nature article was "staggering," requiring editors to spend "inordinate amounts of time" checking submissions they receive.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Biggest Outrage in Atlanta’s Crazy Teacher Cheating Case
- $45 Billion in Tax Dollars Goes Missing in Afghanistan
- How Dark Money Is Distorting Politics and Undermining Democracy
Why Craft Brewers Are Crying in Their Beer

It may be small beer compared to the problems faced by unemployed federal workers and the growing cost for the overall economy, but the ongoing government shutdown is putting a serious crimp in the craft brewing industry. Small-batch brewers tend to produce new products on a regular basis, The Wall Street Journal’s Ruth Simon says, but each new formulation and product label needs to be approved by the Treasury Department’s Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, which is currently closed. So it looks like you’ll have to wait a while to try the new version of Hemperor HPA from Colorado’s New Belgium Brewing, a hoppy brew that will include hemp seeds once the shutdown is over.
Number of the Day: $30 Billion
The amount spent on medical marketing reached $30 billion in 2016, up from $18 billion in 1997, according to a new analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association and highlighted by the Associated Press. The number of advertisements for prescription drugs appearing on television, newspapers, websites and elsewhere totaled 5 million in one year, accounting for $6 billion in marketing spending. Direct-to-consumer marketing grew the fastest, rising from $2 billion, or 12 percent of total marketing, to nearly $10 billion, or a third of spending. “Marketing drives more treatments, more testing” that patients don’t always need, Dr. Steven Woloshin, a Dartmouth College health policy expert and co-author of the study, told the AP.
70% of Registered Voters Want a Compromise to End the Shutdown

An overwhelming majority of registered voters say they want the president and Congress to “compromise to avoid prolonging the government shutdown” in a new The Hill-HarrisX poll. Seven in ten respondents said they preferred the parties reach some sort of deal to end the standoff, while 30 percent said it was more important to stick to principles, even if it means keeping parts of the government shutdown. Voters who “strongly approve” of Trump (a slim 21 percent of respondents) favored him sticking to his principles over the wall by a narrow 54 percent-46 percent margin. Voters who “somewhat approve” of the president favored a compromise solution by a 70-30 margin. Among Republicans overall, 61 percent said they wanted a compromise.
The survey of 1,000 registered voters was conducted January 5 and 6 and has a margin of error of 3.1 percentage points.
Share Buybacks Soar to Record $1 Trillion

Although there may be plenty of things in the GOP tax bill to complain about, critics can’t say it didn’t work – at least as far as stock buybacks go. TrimTabs Investment Research said Monday that U.S. companies have now announced $1 trillion in share buybacks in 2018, surpassing the record of $781 billion set in 2015. "It's no coincidence," said TrimTabs' David Santschi. "A lot of the buybacks are because of the tax law. Companies have more cash to pump up the stock price."
Chart of the Day: Deficits Rising
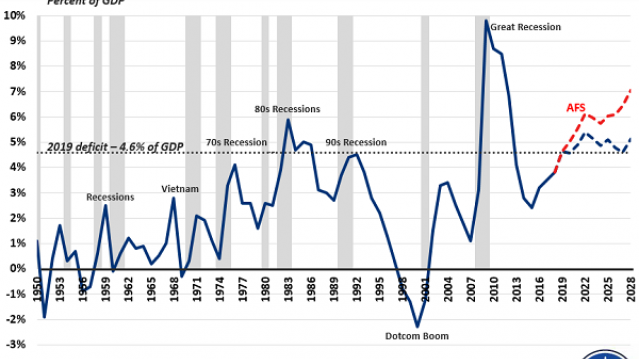
Budget deficits normally rise during recessions and fall when the economy is growing, but that’s not the case today. Deficits are rising sharply despite robust economic growth, increasing from $666 billion in 2017 to an estimated $970 billion in 2019, with $1 trillion annual deficits expected for years after that.
As the deficit hawks at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget point out in a blog post Thursday, “the deficit has never been this high when the economy was this strong … And never in modern U.S. history have deficits been so high outside of a war or recession (or their aftermath).” The chart above shows just how unusual the current deficit path is when measured as a percentage of GDP.
