100-Year-Old Coke Bottle Is About to Become a Movie Star

The Coca-Cola bottle, with its distinctive contoured glass, was created a century ago as a way for the soft drink company to give its product a competitive edge. As the company website explains, “In 1915, Coca-Cola attempted to fend off a host of copycat brands by strengthening its trademark. The company and its bottling partners issued a creative challenge to a handful of U.S. glass companies: To develop a “bottle so distinct that you would recognize if by feel in the dark or lying broken on the ground.”
The winning design, created by the Root Glass Company of Terre Haute, Ind., worked — so well, in fact, that a century later the company is still using that basic concept to market its signature brand. Coca-Cola this year is celebrating the 100th anniversary of the bottle — and its influence in pop art and other realms — through a global advertising campaign, art exhibitions and a photo book, among other avenues.
Now the bottle and its history will also be the subject of a new “authorized” documentary, according to The Hollywood Reporter. (Coke will help pay for the movie’s marketing.)
Related: Why the Soda Industry Is Still Full of Hot Air
“When I can hold up a Coca-Cola bottle and ask, ‘is this art or is this commerce?’ and most commonly hear ‘it’s both,’ that sets the stage for an intriguing narrative,” the movie’s producer and co-director, Matthew Miele, told THR.
That narrative could include how the Coke bottle became the first commercial product to make it to the cover of Time magazine in 1950, or how it provided fodder for artists like Andy Warhol — and, especially if the film touches on today’s backlash against soda, it might even mention that the 10- and 12-ounce bottles that made their debut in 1955 were called “King Size” and a 26-ounce bottle was marketed as “Family Size.”
Miele and his team reportedly hope their documentary will premiere in November to coincide with the Nov. 16, 1915 date that the bottle design first won a patent.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Harsh Truth About Fast Food for Kids
- The Companies Americans Hate Dealing With the Most
- The 15 Worst Supermarkets in America in 2015
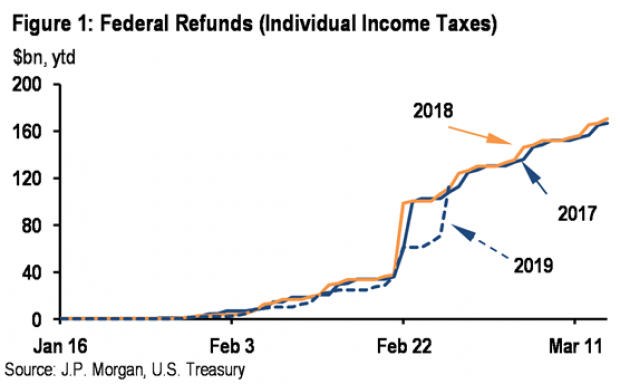
Tax Refunds Rebound

Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
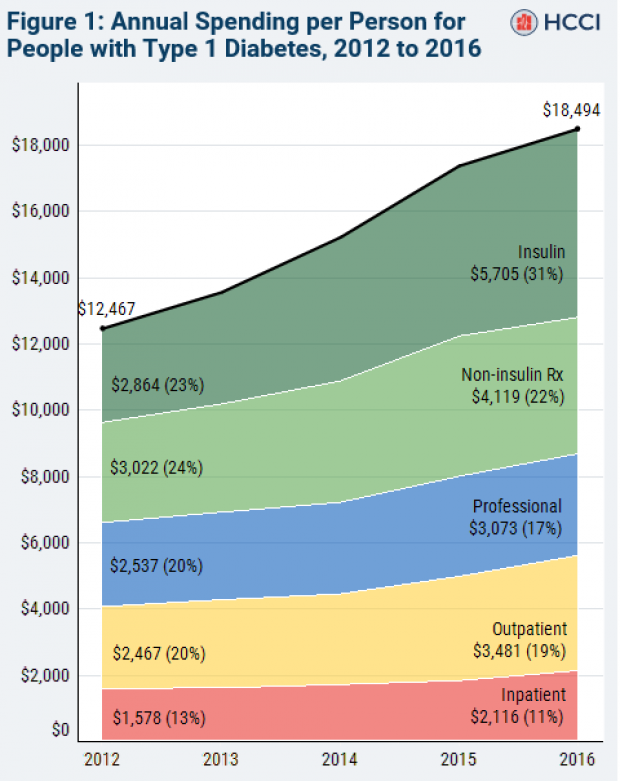
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
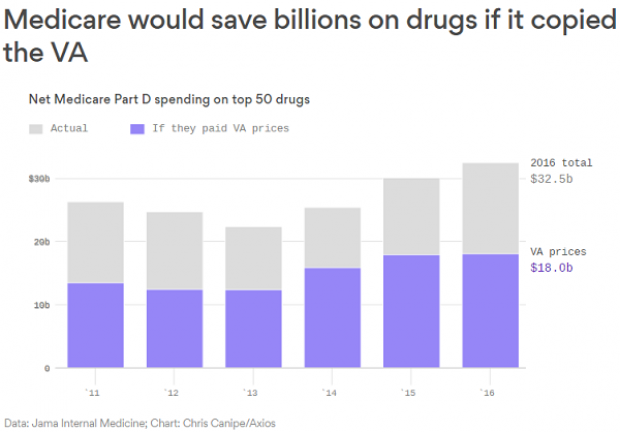
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.