A $180 Million Picasso: What’s Making the Art Market Sizzle
The art market is hotter than a hoisted Rembrandt.
Last night at Christie’s in New York, Picasso’s “Les Femmes d’Alger (Version O)” sold for almost $180 million – the highest price ever paid at auction for a piece of art. There were said to be five bidders, and the winner remains anonymous.
At the same sale, a Giacometti sculpture, “L’homme au doigt,” went for a total of more than $141 million.
On May 5, at the first major auction of the spring selling season, Sotheby’s pulled in $368 million. It was the second-highest sale of Impressionist and modern art in the history of the auction house, according to The New York Times. The top seller was van Gogh’s “L’allée Des Alyscamps,” which fetched $66.3 million.
Related: 6 Traits of an Emerging Millionaire. Are you one?
The haul represented a 67 percent increase over Sotheby’s spring sale a year earlier, according to Bloomberg, which noted that many of the buyers were Asian.
The May 5 auction was only the second-highest because Sotheby’s held a sale last November that took in $422 million.
And tonight at a Sotheby’s auction of contemporary art, a painting entitled “The Ring (Engagement)” by the Pop artist Roy Lichtenstein could sell for as much as $50 million, the Times said.
What’s behind all those staggering numbers?
About a year and a half ago, the columnist Felix Salmon (then at Reuters, now at Fusion) ruminated about whether there was a bubble, which he defined as often driven by FOMO (fear of missing out), or a speculative bubble, one fueled by flippers, in the art market. His conclusion: the art market bubble was definitely not speculative.
“The people spending millions of dollars on trophy art aren’t buying to flip…,” he wrote.
Related: Get Ready for Another Real Estate Bubble
Still, Salmon said he was seeing signs that the market could be turning speculative. But they may have been false signals.
Recently, The Wall Street Journal wrote: “Spurred by the momentum of several successful sale seasons and an influx of newly wealthy global bidders, the major auction houses…say demand for status art is at historic levels and shows no signs of tapering off.”
But why?
In an April 17 article, the global news website Worldcrunch asked Financial Times journalist Georgina Adam, who wrote the 2014 book Big Bucks—The Explosion of the Art Market in the 21st Century, why so much money is rolling around the art market and driving up prices.
“Rich people used to be rich in terms of estate or assets, but not so much in terms of cash, like they are today,” she said.
“This growing billionaire population from developed or developing economies has money to spend and invest,” said the Worldcrunch article by Catherine Cochard. “For many of them, art — in the same way as luxury cars or prêt-à-porter — is an entry pass to a globalized way of life accessible through their wealth.”
That is a development that the keen eyes at the auction houses haven’t missed.
Why Craft Brewers Are Crying in Their Beer

It may be small beer compared to the problems faced by unemployed federal workers and the growing cost for the overall economy, but the ongoing government shutdown is putting a serious crimp in the craft brewing industry. Small-batch brewers tend to produce new products on a regular basis, The Wall Street Journal’s Ruth Simon says, but each new formulation and product label needs to be approved by the Treasury Department’s Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, which is currently closed. So it looks like you’ll have to wait a while to try the new version of Hemperor HPA from Colorado’s New Belgium Brewing, a hoppy brew that will include hemp seeds once the shutdown is over.
Number of the Day: $30 Billion
The amount spent on medical marketing reached $30 billion in 2016, up from $18 billion in 1997, according to a new analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association and highlighted by the Associated Press. The number of advertisements for prescription drugs appearing on television, newspapers, websites and elsewhere totaled 5 million in one year, accounting for $6 billion in marketing spending. Direct-to-consumer marketing grew the fastest, rising from $2 billion, or 12 percent of total marketing, to nearly $10 billion, or a third of spending. “Marketing drives more treatments, more testing” that patients don’t always need, Dr. Steven Woloshin, a Dartmouth College health policy expert and co-author of the study, told the AP.
70% of Registered Voters Want a Compromise to End the Shutdown

An overwhelming majority of registered voters say they want the president and Congress to “compromise to avoid prolonging the government shutdown” in a new The Hill-HarrisX poll. Seven in ten respondents said they preferred the parties reach some sort of deal to end the standoff, while 30 percent said it was more important to stick to principles, even if it means keeping parts of the government shutdown. Voters who “strongly approve” of Trump (a slim 21 percent of respondents) favored him sticking to his principles over the wall by a narrow 54 percent-46 percent margin. Voters who “somewhat approve” of the president favored a compromise solution by a 70-30 margin. Among Republicans overall, 61 percent said they wanted a compromise.
The survey of 1,000 registered voters was conducted January 5 and 6 and has a margin of error of 3.1 percentage points.
Share Buybacks Soar to Record $1 Trillion

Although there may be plenty of things in the GOP tax bill to complain about, critics can’t say it didn’t work – at least as far as stock buybacks go. TrimTabs Investment Research said Monday that U.S. companies have now announced $1 trillion in share buybacks in 2018, surpassing the record of $781 billion set in 2015. "It's no coincidence," said TrimTabs' David Santschi. "A lot of the buybacks are because of the tax law. Companies have more cash to pump up the stock price."
Chart of the Day: Deficits Rising
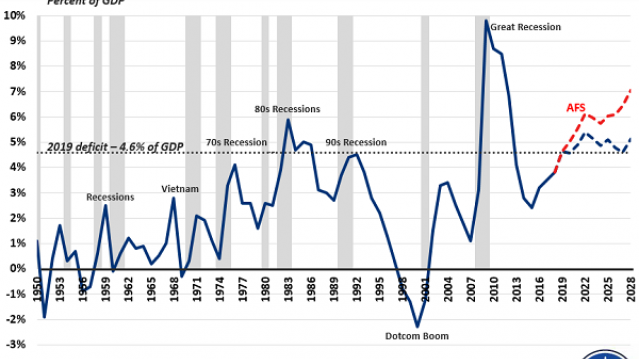
Budget deficits normally rise during recessions and fall when the economy is growing, but that’s not the case today. Deficits are rising sharply despite robust economic growth, increasing from $666 billion in 2017 to an estimated $970 billion in 2019, with $1 trillion annual deficits expected for years after that.
As the deficit hawks at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget point out in a blog post Thursday, “the deficit has never been this high when the economy was this strong … And never in modern U.S. history have deficits been so high outside of a war or recession (or their aftermath).” The chart above shows just how unusual the current deficit path is when measured as a percentage of GDP.
