Go to Work, Ladies! Your Kids Will Be Grateful

So what if you can’t have it all? Maybe your daughter can.
A new working paper by the Harvard Business School finds that daughters of working mothers are likely to be more successful in the workplace than their peers. Analyzing data on 50,000 people in 24 countries, researchers found these women are more likely to be employed, hold supervisory positions and earn more money than women who grew up with stay-at-home mothers.
A working mother was defined as being employed before their child turned 14 years old.
Daughters of employed moms are 4.5 percent more likely than daughters of stay-at-home moms have jobs, the study found -- small but statistically significant difference, the authors say, meaning it’s not just a coincidence. Daughters of working mothers also earn 23 percent more than daughters of women did not work outside the home.
Related: 10 Best States for Working Mothers
In addition, 33 percent of daughters of employed women hold supervisory roles, compared to 25 percent of daughters of stay-at-home mothers. And the daughters of working moms do fewer hours of housework each week, the study finds.
Sons of working mothers were found to spend 7.5 more hours on childcare per week and a longer amount of time on household chores. They spend more time caring for family members than sons of stay-at-home mothers.
The study hints at the neglected importance of gender attitudes that are shaped and refined within homes and in families, since policymakers usually focus on gender differences on the political and corporate levels. Parents who embody non-traditional gender roles are serving as role models and a resource for their children who might one day enact non-traditional gender roles in their own lives.
Working mothers are demonstrating to their children that traditional gender roles are not the only opportunities for their sons or daughters. Even though many mothers worry that by working they’re neglecting their child, they could actually be helping them in the long-run by showing them they’re world might not be as limited as tradition suggests.
The study comes in the wake of a slight reversal in the decades-long trend of women joining the ranks of the employed. From 1999 to 2012, the number of mothers who were unemployed in the U.S. rose from 23 percent to 29 percent, a Pew study found. Causes of the rise are debatable, but a growing number of women cite their inability to find a job, largely as the result of the recession.
With the job market recovering, the new study’s message is clear: Lean in, women!
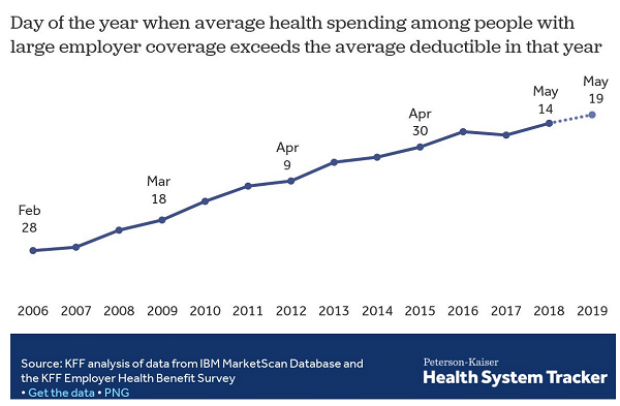
Coming Soon: Deductible Relief Day!

You may be familiar with the concept of Tax Freedom Day – the date on which you have earned enough to pay all of your taxes for the year. Focusing on a different kind of financial burden, analysts at the Kaiser Family Foundation have created Deductible Relief Day – the date on which people in employer-sponsored insurance plans have spent enough on health care to meet the average annual deductible.
Average deductibles have more than tripled over the last decade, forcing people to spend more out of pocket each year. As a result, Deductible Relief Day is “getting later and later in the year,” Kaiser’s Larry Levitt said in a tweet Thursday.
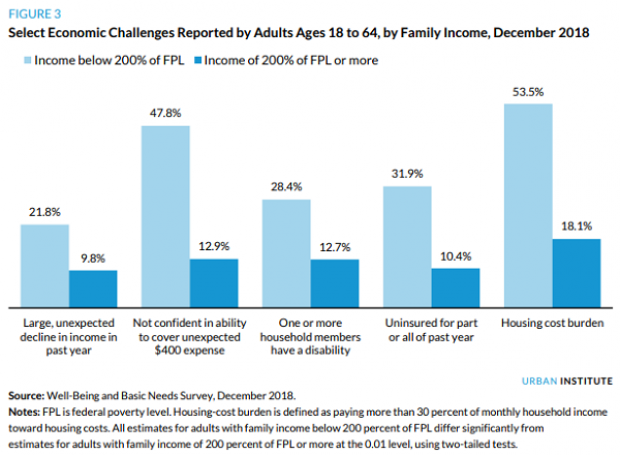
Chart of the Day: Families Still Struggling

Ten years into what will soon be the longest economic expansion in U.S. history, 40% of families say they are still struggling, according to a new report from the Urban Institute. “Nearly 4 in 10 nonelderly adults reported that in 2018, their families experienced material hardship—defined as trouble paying or being unable to pay for housing, utilities, food, or medical care at some point during the year—which was not significantly different from the share reporting these difficulties for the previous year,” the report says. “Among adults in families with incomes below twice the federal poverty level (FPL), over 60 percent reported at least one type of material hardship in 2018.”
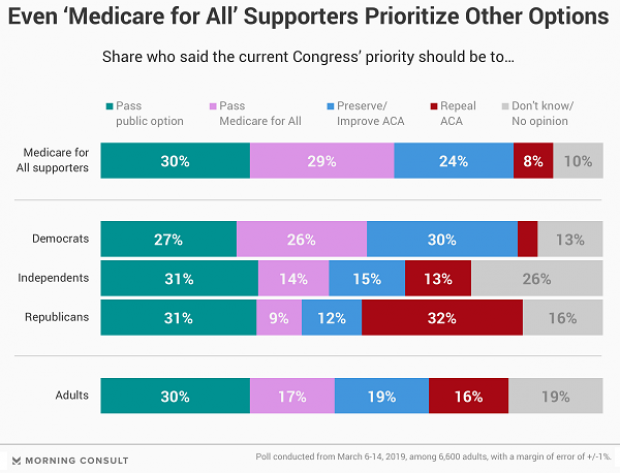
Chart of the Day: Pragmatism on a Public Option

A recent Morning Consult poll 3,073 U.S. adults who say they support Medicare for All shows that they are just as likely to back a public option that would allow Americans to buy into Medicare or Medicaid without eliminating private health insurance. “The data suggests that, in spite of the fervor for expanding health coverage, a majority of Medicare for All supporters, like all Americans, are leaning into their pragmatism in response to the current political climate — one which has left many skeptical that Capitol Hill can jolt into action on an ambitious proposal like Medicare for All quickly enough to wrangle the soaring costs of health care,” Morning Consult said.
Chart of the Day: The Explosive Growth of the EITC

The Earned Income Tax Credit, a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income workers, was established in 1975, with nominal claims of about $1.2 billion ($5.6 billion in 2016 dollars) in its first year. According to the Tax Policy Center, by 2016 “the total was $66.7 billion, almost 12 times larger in real terms.”
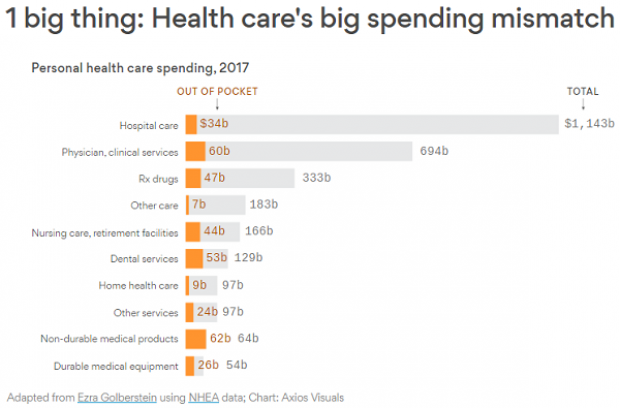
Chart of the Day: The Big Picture on Health Care Costs

“The health care services that rack up the highest out-of-pocket costs for patients aren't the same ones that cost the most to the health care system overall,” says Axios’s Caitlin Owens. That may distort our view of how the system works and how best to fix it. For example, Americans spend more out-of-pocket on dental services ($53 billion) than they do on hospital care ($34 billion), but the latter is a much larger part of national health care spending as a whole.