Did Airlines Collude to Keep Air Fares High?

For months now, oil and gas prices have been dropping—and that includes jet fuel. So why haven’t airline ticket prices dropped as well? That’s one of the questions the Justice Department wants answered as it investigates the possibility of collusion among carriers to keep airfares high.
The DOJ also wants to know if companies conspired to limit the number of available seats in order to drive prices up. Yesterday, the Associated Press broke the news that major U.S. carriers had received a letter demanding copies of all communications the airlines had with each other, Wall Street analysts, and major shareholders about their plans for passenger-carrying capacity, going back to January 2010. The civil antitrust investigation is focusing on whether airlines illegally indicated to each other how quickly they would add new flights, routes, and extra seats in an effort to prop up ticket prices.
Related: 6 Sneaky Fees That Are Making Airlines a Bundle
Just minutes after the news broke, stocks of the major U.S. airlines fell four to five percent, with the S&P 500 airlines index off more than four percent. Until now, the U.S. airline industry had been enjoying record profits, due to increasing numbers of Americans flying and a huge drop in the price of jet fuel. In April, the price of jet fuel was $1.94 per gallon, a decrease of 34 percent from the previous year.
The investigation marks a notable shift for the Justice Department, which approved the merger of American Airlines and US Airways back in November 2013, despite previously blocking it over concerns that the airlines would collude on fares. The probe could signal a more aggressive approach on antitrust enforcement, under the strong leadership of Loretta Lynch, who was confirmed in April.
Justice Department spokesperson Emily Pierce confirmed that the department was investigating potential “unlawful coordination” among some airlines.
Just two weeks ago, U.S. Senator Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) urged the Justice Department to investigate what he called “anti-competitive, anti-consumer conduct and misuse of market power in the airline industry.”
Related: United Airlines Bullish on First Quarter from Lower Fuel Costs
Since 2008, various mergers have resulted in four major airlines (down from nine)—American, Delta, Southwest, and United—controlling about 80 percent of all domestic air travel. All four airlines have confirmed that they received the letter and that they were cooperating with the investigation.
According to Bureau of Transportation Statistics, the average domestic airfare rose 13 percent from 2009 to 2014 (adjusted for inflation). The average domestic flight last year cost $391. In the past year alone, airlines received an additional $3.6 billion from bag fees and another $3 billion from reservation-change fees. All of the major airlines—American Airlines, United Continental Holdings, Delta Air Lines, Southwest Airlines, JetBlue Airways, and Alaska Air Group—posted record profits with a consolidated net income of over $3 billion during the first quarter of 2015.
Budget ‘Chaos’ Threatens Army Reset: Retired General
One thing is standing in the way of a major ongoing effort to reset the U.S. Army, writes Carter Ham, a retired four-star general who’s now president and CEO of the Association of the U.S. Army, at Defense One. “The problem is the Washington, D.C., budget quagmire.”
The issue is more than just a matter of funding levels. “What hurts more is the erratic, unreliable and downright harmful federal budget process,” which has forced the Army to plan based on stopgap “continuing resolutions” instead of approved budgets for nine straight fiscal years. “A slowdown in combat-related training, production delays in new weapons, and a postponement of increases in Army troop levels are among the immediate impacts of operating under this ill-named continuing resolution. It’s not continuous and it certainly doesn’t display resolve.”
Pentagon Pushes for Faster F-35 Cost Cuts

The Pentagon has taken over cost-cutting efforts for the F-35 program, which has been plagued by years of cost overruns, production delays and technical problems. The Defense Department rejected a cost-saving plan proposed by contractors including principal manufacturer Lockheed Martin as being too slow to produce substantial savings. Instead, it gave Lockheed a $60 million contract “to pursue further efficiency measures, with more oversight of how the money was spent,” The Wall Street Journal’s Doug Cameron reports. F-35 program leaders “say they want more of the cost-saving effort directed at smaller suppliers that haven’t been pressured enough.” The Pentagon plans to cut the price of the F-35A model used by the Air Force from a recent $94.6 million each to around $80 million by 2020. Overall, the price of developing the F-35 has climbed above $400 billion, with the total program cost now projected at $1.53 trillion. (Wall Street Journal, CNBC)
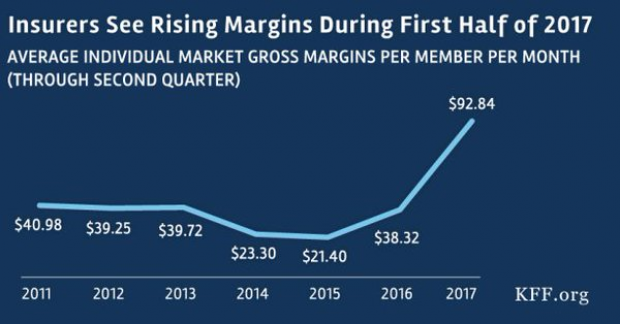
Chart of the Day - October 6, 2017
Financial performance for insurers in the individual Obamacare markets is improving, driven by higher premiums and slower growth in claims. This suggests that the market is stabilizing. (Kaiser Family Foundation)
Quote of the Day - October 5, 2017
"The train's left the station, and if you're a budget hawk, you were left at the station." -- Rep. Mark Sanford, R-S.C.