Looking for Likes? When to Post on Facebook for Maximum Attention

Trying to decide when to post photo updates to your “Summer 2015” album so the maximum number of people click through, comment on, and like your filtered selfies? Look no further. A new study conducted by the social media analytics firm Klout can tell you the best time and day of the week to post on Facebook and Twitter, depending where you are in the world.
The study found that posting in the late morning and early afternoons on Tuesdays and Wednesdays tends to generate the most engagement. Thursdays tend to be quiet, Fridays are quieter still, and the weekends are the quietest. On Mondays, the activity level begins to ramp up again as the work week begins and bored office workers take social media breaks.
Optimal times also depend on location. Tokyo peaks at the earliest time among cities studied, between 7 a.m. and 9 a.m. Paris has a high level of engagement once in the morning and once in the afternoon. In San Francisco, between 9 a.m. and 10 a.m. is ideal for posting. The most favorable time in New York is just before noon. London peaks the latest, with users becoming fully engaged on Twitter and Facebook only in the early afternoon.
Thinking about posting a picture of your cute new nephew at night? Don’t even bother if you want maximum engagement from your followers and friends. While one explanation is that fewer people are online at night, another is that most likes, shares, and comments occur within a short window of time after someone posts something. Researchers of the study found the majority of reactions were within the first two hours of posting time.
Using a sample set of half a million active users and more than 25 million messages over 56 days, the report boasts a reaction gain of up to 4 percent on Twitter and 17 percent on Facebook when the recommended posting times are used.
Why Craft Brewers Are Crying in Their Beer

It may be small beer compared to the problems faced by unemployed federal workers and the growing cost for the overall economy, but the ongoing government shutdown is putting a serious crimp in the craft brewing industry. Small-batch brewers tend to produce new products on a regular basis, The Wall Street Journal’s Ruth Simon says, but each new formulation and product label needs to be approved by the Treasury Department’s Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, which is currently closed. So it looks like you’ll have to wait a while to try the new version of Hemperor HPA from Colorado’s New Belgium Brewing, a hoppy brew that will include hemp seeds once the shutdown is over.
Number of the Day: $30 Billion
The amount spent on medical marketing reached $30 billion in 2016, up from $18 billion in 1997, according to a new analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association and highlighted by the Associated Press. The number of advertisements for prescription drugs appearing on television, newspapers, websites and elsewhere totaled 5 million in one year, accounting for $6 billion in marketing spending. Direct-to-consumer marketing grew the fastest, rising from $2 billion, or 12 percent of total marketing, to nearly $10 billion, or a third of spending. “Marketing drives more treatments, more testing” that patients don’t always need, Dr. Steven Woloshin, a Dartmouth College health policy expert and co-author of the study, told the AP.
70% of Registered Voters Want a Compromise to End the Shutdown

An overwhelming majority of registered voters say they want the president and Congress to “compromise to avoid prolonging the government shutdown” in a new The Hill-HarrisX poll. Seven in ten respondents said they preferred the parties reach some sort of deal to end the standoff, while 30 percent said it was more important to stick to principles, even if it means keeping parts of the government shutdown. Voters who “strongly approve” of Trump (a slim 21 percent of respondents) favored him sticking to his principles over the wall by a narrow 54 percent-46 percent margin. Voters who “somewhat approve” of the president favored a compromise solution by a 70-30 margin. Among Republicans overall, 61 percent said they wanted a compromise.
The survey of 1,000 registered voters was conducted January 5 and 6 and has a margin of error of 3.1 percentage points.
Share Buybacks Soar to Record $1 Trillion

Although there may be plenty of things in the GOP tax bill to complain about, critics can’t say it didn’t work – at least as far as stock buybacks go. TrimTabs Investment Research said Monday that U.S. companies have now announced $1 trillion in share buybacks in 2018, surpassing the record of $781 billion set in 2015. "It's no coincidence," said TrimTabs' David Santschi. "A lot of the buybacks are because of the tax law. Companies have more cash to pump up the stock price."
Chart of the Day: Deficits Rising
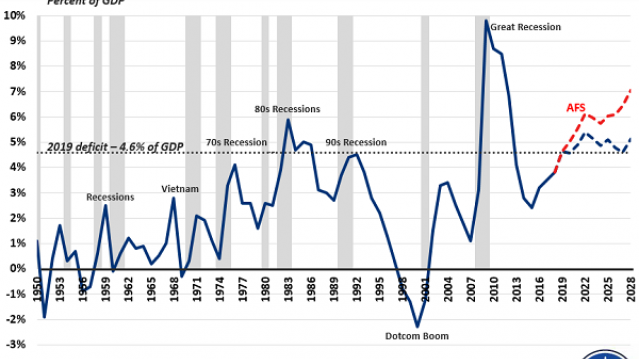
Budget deficits normally rise during recessions and fall when the economy is growing, but that’s not the case today. Deficits are rising sharply despite robust economic growth, increasing from $666 billion in 2017 to an estimated $970 billion in 2019, with $1 trillion annual deficits expected for years after that.
As the deficit hawks at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget point out in a blog post Thursday, “the deficit has never been this high when the economy was this strong … And never in modern U.S. history have deficits been so high outside of a war or recession (or their aftermath).” The chart above shows just how unusual the current deficit path is when measured as a percentage of GDP.
