Why We All Buy Tide: The 10 Biggest Advertisers in the U.S.

The 200 top national advertisers spent a record $137.8 billion last year trying to get you to buy more of their goods and services, an increase of 2 percent over 2013, according to Ad Age’s latest annual spending review.
That total was slightly more than the GDP of Hungary last year, but the growth rate was the lowest since 2009, as advertisers looked to get the most for their money. Internet display advertising among those 200 marketing Goliaths dropped by 13.3 percent.
Overall, 38 marketers spent more than $1 billion on advertising last year. Procter & Gamble remains the country’s (and the world’s) largest advertiser. It shelled out $4.6 billion in the U.S. alone to promote brands such as Crest, Duracell, Pampers and Tide — or well over $1 billion more than the next biggest spender. P&G’s CFO recently revealed plans to cut ad spending by as much as $500 million, though.
Here’s Ad Age’s list of the 10 biggest advertisers in the U.S. last year:
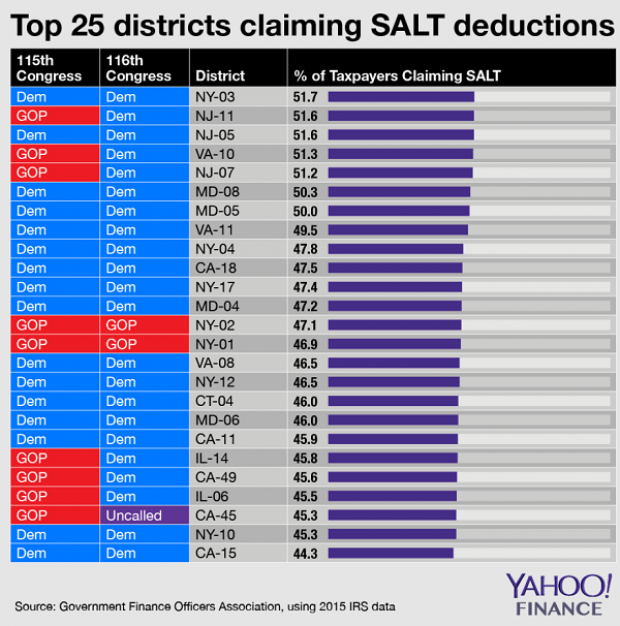
Chart of the Day: SALT in the GOP’s Wounds

The stark and growing divide between urban/suburban and rural districts was one big story in this year’s election results, with Democrats gaining seats in the House as a result of their success in suburban areas. The GOP tax law may have helped drive that trend, Yahoo Finance’s Brian Cheung notes.
The new tax law capped the amount of state and local tax deductions Americans can claim in their federal filings at $10,000. Congressional seats for nine of the top 25 districts where residents claim those SALT deductions were held by Republicans heading into Election Day. Six of the nine flipped to the Democrats in last week’s midterms.
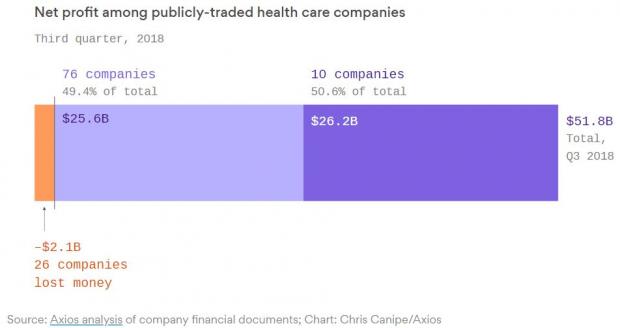
Chart of the Day: Big Pharma's Big Profits
Ten companies, including nine pharmaceutical giants, accounted for half of the health care industry's $50 billion in worldwide profits in the third quarter of 2018, according to an analysis by Axios’s Bob Herman. Drug companies generated 23 percent of the industry’s $636 billion in revenue — and 63 percent of the total profits. “Americans spend a lot more money on hospital and physician care than prescription drugs, but pharmaceutical companies pocket a lot more than other parts of the industry,” Herman writes.
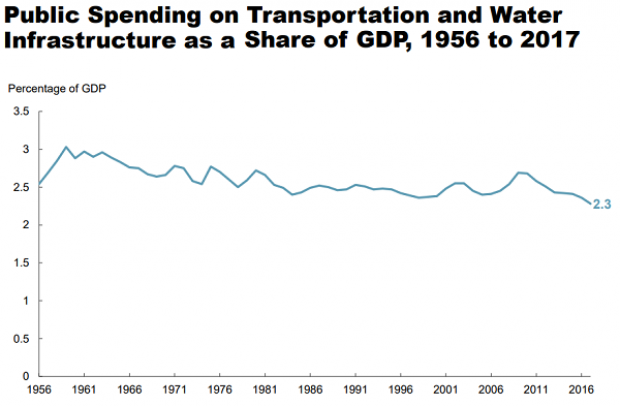
Chart of the Day: Infrastructure Spending Over 60 Years

Federal, state and local governments spent about $441 billion on infrastructure in 2017, with the money going toward highways, mass transit and rail, aviation, water transportation, water resources and water utilities. Measured as a percentage of GDP, total spending is a bit lower than it was 50 years ago. For more details, see this new report from the Congressional Budget Office.
Number of the Day: $3.3 Billion

The GOP tax cuts have provided a significant earnings boost for the big U.S. banks so far this year. Changes in the tax code “saved the nation’s six biggest banks $3.3 billion in the third quarter alone,” according to a Bloomberg report Thursday. The data is drawn from earnings reports from Bank of America, Citigroup, Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, Morgan Stanley and Wells Fargo.
Clarifying the Drop in Obamacare Premiums

We told you Thursday about the Trump administration’s announcement that average premiums for benchmark Obamacare plans will fall 1.5 percent next year, but analyst Charles Gaba says the story is a bit more complicated. According to Gaba’s calculations, average premiums for all individual health plans will rise next year by 3.1 percent.
The difference between the two figures is produced by two very different datasets. The Trump administration included only the second-lowest-cost Silver plans in 39 states in its analysis, while Gaba examined all individual plans sold in all 50 states.