Can Anyone Stop the $38 Billion Airline Fee Squeeze?

U.S. airlines earned $2.6 billion in fees and frequent flier mile sales in 2014, an 18.7 percent increase from 2013, according to an annual report by consultancies IdeaWorks and CarTrawler.
That represents the eighth consecutive year that carriers saw substantial revenue ancillary to ticket sales. Globally, ancillary revenue soared more than 20 percent to $38.1 billion.
“Ancillary revenue is an increasingly important indicator of commercial success, and a major contributor to the bottom line of airlines across the globe,” said Michael Cunningham, CarTrawler’s Chief Commercial Officer, in a statement.
Related: 6 Sneaky Fees that Are Making Airlines a Bundle
By passenger, additional revenue grew by 8.5 percent to $17.49. Low cost carriers increased ancillary revenue by 32.8 percent for the year, or $2.9 billion.
Ten airlines earned two-thirds of the ancillary revenue, led by United Airlines, American/U.S. Airways, and Delta. Delta brought in $350 million through its Comfort Plus program, which allows passengers to pay extra for more legroom and priority boarding.
Among passengers’ most hated fees are checked bag fees. Airlines typically charge $25 for the first bag, $35 for the second, and more than $100 for a third bag.
As frequent fliers turn to branded credit cards as a means of avoiding fees, airlines are still earning money. Last year, American’s Citibank-issued credit card, which gives consumers one free checked bag and priority boarding, yielded an additional $624 million for the carrier last year.
The additional fees are not improving the customer experience. More than 60 percent of consumers surveyed by the U.S. Travel Association in March said they were frustrated with air travel generally.
Economists See More Growth Ahead

Most business economists in the U.S. expect the economy to keep chugging along over the next three months, with rising corporate sales driving additional hiring and wage increases for workers.
The tax cuts, however, don’t seem to be playing a role in hiring and investment plans. And the trade conflicts stirred up by the Trump administration are having a negative influence, with the majority of economists at goods-producing firms who replied to the most recent survey by the National Association for Business Economics saying that their companies were putting investments on hold as they wait to see how things play out.
New Tax on Non-Profits Hits Public Universities

The Republican tax bill signed into law late last year imposed a 21 percent tax on employees at non-profits who earn more than $1 million a year. According to data from the Chronicle of Higher Education cited by Bloomberg, there were 12 presidents of public universities who received compensation of at least $1 million in 2017, with James Ramsey of the University of Louisville topping the list at $4.3 million. Endowment managers could also get hit with the tax, as could football coaches, some of whom earn substantially more than the presidents of their institutions.
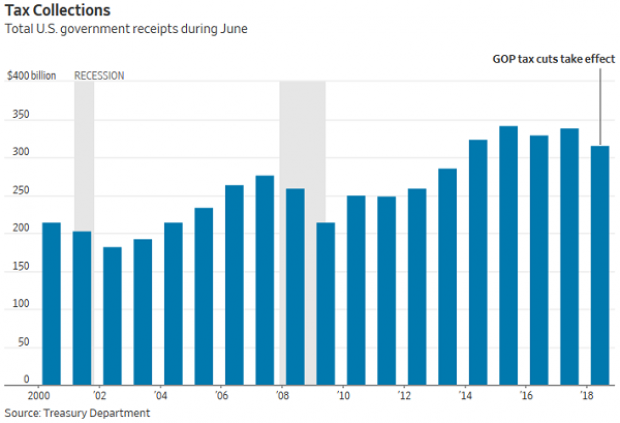
Government Revenues Drop as Tax Cuts Kick In

Corporate tax receipts in June were 33 percent lower than a year ago, according to data released by the Treasury Department Thursday, as companies made smaller estimated payments due to the reduction in their tax rates. Total receipts were down 7 percent, while payroll taxes were 5 percent lower compared to June 2017.
“June receipts to US government were our first mostly-clear look at the revenue effects of the new tax law, with lots of estimated payments and little noise from the 2017 tax year,” The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin tweeted Friday.
Surprisingly, the deficit was smaller in June compared to a year ago, narrowing to $74.86 billion from $90.23 billion last year. The drop was driven by a 9 percent reduction in government outlays that reflected accounting changes rather than any real changes in spending, Rubin said in the Journal.
“More broadly, the federal deficit is swelling as government spending outpaces revenues,” Rubin wrote. “The budget gap totaled $607.1 billion in the first nine months of the 2018 fiscal year, 16% larger than the same point a year earlier.”
Kyle Pomerleau of the Tax Foundation pointed out that the drop in corporate tax receipts is a permanent feature of the Republican tax cuts, tweeting: “Even in a Trump dream world in which these cuts paid for themselves, corporate tax collections would remain below baseline forever. It would be higher income and payroll receipts that made up the difference.”
Deficit Jumps in Trump’s First Fiscal Year

The federal budget deficit rose by 16 percent in the first nine months of the 2018 fiscal year, which began last October. The shortfall came to $607 billion, compared to $523 billion in the same period the year before, according to a U.S. Treasury report released Thursday and reported by Bloomberg. Both revenue and spending rose, but spending rose faster. Revenues came to $2.54 trillion, up 1.3 percent from the same nine-month period in 2017, while spending came to $3.15 trillion, up 3.9 percent.
Where’s the Obamacare Navigator Funding for 2019, PA Insurance Commissioner Asks
Pennsylvania’s insurance commissioner sent a letter this week to Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Administrator Seema Verma requesting that they “immediately release the funding details for the Navigator program for the upcoming open enrollment period for 2019.” Navigators are the state and local groups that help people sign up for Affordable Care Act plans.
“In years past, grant applications and new funding opportunities were released by CMS in April, CMS required Navigator organizations to apply by June and approved applications and new funding by late August,” Pennsylvania’s Jessica Altman wrote. “The current lack of guidance has put Navigator organizations – and states - far behind in their planning and creates an inability for the Navigator organizations to design a successful plan for helping people enroll during the 2019 open enrollment period.”