Why Investors Prefer Real Estate to Stocks, Bond and Gold

Americans still feel skittish about the stock market. When it comes to long-term investments, real estate is still preferred over cash or the stock market, Bankrate.com reports in a new study. For long term investments over 10 years or more, 27 percent chose real estate, 23 percent preferred cash investments, and 17 percent opted for the stock market. Gold and precious metals came in fourth at 14 percent, and bonds debuted at 5 percent.
Related: Clinton’s Capital Gains Tax Plan Aims at Long-Term Investment
Although the S&P 500 has risen 27 percent over the past two years, Americans were only slightly more inclined to favor stocks in 2015 than they were in 2013.
The only exception to the brick and mortar policy? Households headed by college graduates were the most likely to prefer stocks. In the western U.S., real estate was preferred nearly two to one over any other investment choice.
The survey of 1,000 adults living in the continental U.S. yielded some surprises across gender, age, income, location, and political party. Men were more likely to favor real estate, while women were more likely to favor cash investments.
At 32 percent, the majority of millennials--those between 18 and 29 years old--favored cold, hard cash, while 32 percent of participants between the ages of 30 and 40 stuck with real estate.
Related: U.S. Real Estate ETF Rally Faces Test With Rate Rise
Lower-income workers with salaries of less than $50,000 felt “more secure” than their higher earning counterparts, who were making $50,000 to $74,900. And Republicans were three times more likely to say they felt “less secure” about their jobs as Democrats.
Bankrate’s Financial Security Index for July remained positive for the 14th consecutive month. However the July reading was the second lowest in 2015, due in part to a decline in job security with 22 percent feeling “more secure” about their jobs than 12 months ago and 14 percent feeling “less secure.” Sixty-two percent felt “about the same.”
Tax Refunds Rebound

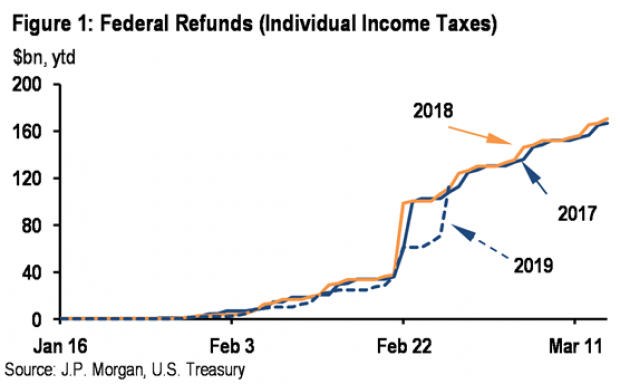
Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
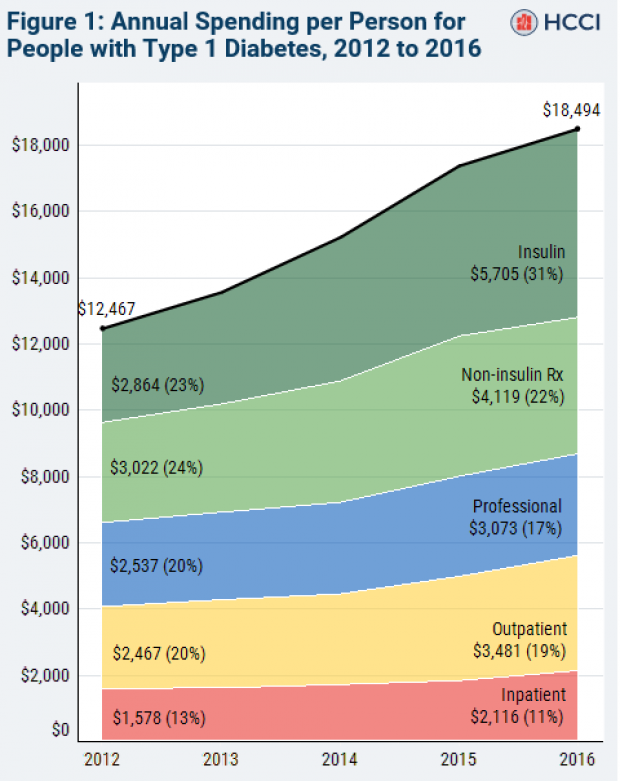
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
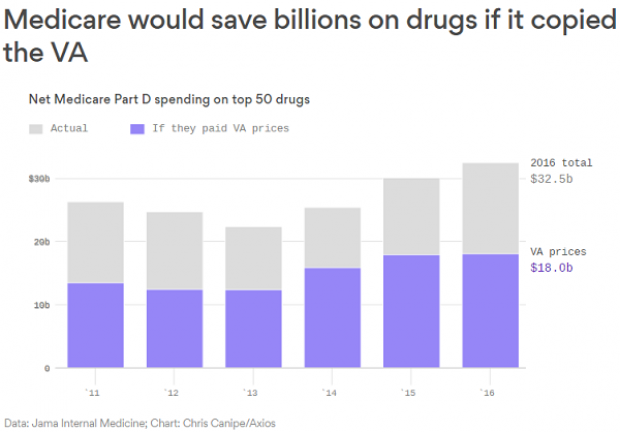
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.