Worried About a Recession? Here’s When the Next Slump Will Hit

The next recession may be coming sooner than you think.
Eleven of the 31 economists recently surveyed by Bloomberg believed the American recession would hit in 2018, and all but two of them expected the recession to begin within the next five years.
If the recession begins in 2018, the expansion would have lasted nine years, making it the second-longest period of growth in U.S. history after the decade-long expansion that ended when the tech bubble burst in 2001. This average postwar expansion averages about five years.
The recent turmoil in the stock market and the slowdown in China has more investors and analysts using the “R-word,” but the economists surveyed by Bloomberg think we have a bit of time. They pegged the chance of recession over the next 12 months to just 10 percent.
Related: Stocks Are Sending a Recession Warning
While economists talk about the next official recession, many average Americans feel like they’re still climbing out of the last one. In a data brief released last week, the National Employment Law Project found that wages have declined since 2009 for most U.S. workers, when factoring in cost of living increases.
A full jobs recovery is at least two years away, according to an analysis by economist Elise Gould with the Economic Policy Institute. “Wage growth needs to be stronger—and consistently strong for a solid spell—before we can call this a healthy economy,” she wrote in a recent blog post.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- This CEO Makes 1,951 Times More Than Most of His Workers
- Seven Reasons Why the Fed Won’t Hike Interest Rates
- $42 Million for 54 Recruits: U.S. Program to Train Syrian Rebels Is a Disaster
Budget ‘Chaos’ Threatens Army Reset: Retired General
One thing is standing in the way of a major ongoing effort to reset the U.S. Army, writes Carter Ham, a retired four-star general who’s now president and CEO of the Association of the U.S. Army, at Defense One. “The problem is the Washington, D.C., budget quagmire.”
The issue is more than just a matter of funding levels. “What hurts more is the erratic, unreliable and downright harmful federal budget process,” which has forced the Army to plan based on stopgap “continuing resolutions” instead of approved budgets for nine straight fiscal years. “A slowdown in combat-related training, production delays in new weapons, and a postponement of increases in Army troop levels are among the immediate impacts of operating under this ill-named continuing resolution. It’s not continuous and it certainly doesn’t display resolve.”
Pentagon Pushes for Faster F-35 Cost Cuts

The Pentagon has taken over cost-cutting efforts for the F-35 program, which has been plagued by years of cost overruns, production delays and technical problems. The Defense Department rejected a cost-saving plan proposed by contractors including principal manufacturer Lockheed Martin as being too slow to produce substantial savings. Instead, it gave Lockheed a $60 million contract “to pursue further efficiency measures, with more oversight of how the money was spent,” The Wall Street Journal’s Doug Cameron reports. F-35 program leaders “say they want more of the cost-saving effort directed at smaller suppliers that haven’t been pressured enough.” The Pentagon plans to cut the price of the F-35A model used by the Air Force from a recent $94.6 million each to around $80 million by 2020. Overall, the price of developing the F-35 has climbed above $400 billion, with the total program cost now projected at $1.53 trillion. (Wall Street Journal, CNBC)
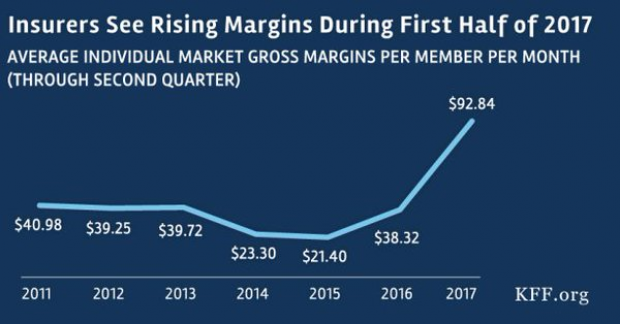
Chart of the Day - October 6, 2017
Financial performance for insurers in the individual Obamacare markets is improving, driven by higher premiums and slower growth in claims. This suggests that the market is stabilizing. (Kaiser Family Foundation)
Quote of the Day - October 5, 2017
"The train's left the station, and if you're a budget hawk, you were left at the station." -- Rep. Mark Sanford, R-S.C.