The Hidden Tax Bracket in the GOP Plan

Politico’s Danny Vinik: “Thanks to a quirky proposed surcharge, Americans who earn more than $1 million in taxable income would trigger an extra 6 percent tax on the next $200,000 they earn—a complicated change that effectively creates a new, unannounced tax bracket of 45.6 percent. … The new rate stems from a provision in the bill intended to help the government recover, from the very wealthy, some of the benefits that lower-income taxpayers enjoy. … After the first $1 million in taxable income, the government would impose a 6 percent surcharge on every dollar earned, until it made up for the tax benefits that the rich receive from the low tax rate on that first $45,000. That surcharge remains until the government has clawed back the full $12,420, which would occur at about $1.2 million in taxable income. At that point, the surcharge disappears and the top tax rate drops back to 39.6 percent.”
Vinik writes that the surcharge would have affected more than 400,000 tax filers in 2015, according to IRS data, and that it could raise more than $50 billion in revenue over a decade. At a Politico event Friday, House Ways and Means Chairman Kevin Brady said the surcharge, sometimes called a bubble rate, was included to try to drive more middle-class tax relief.
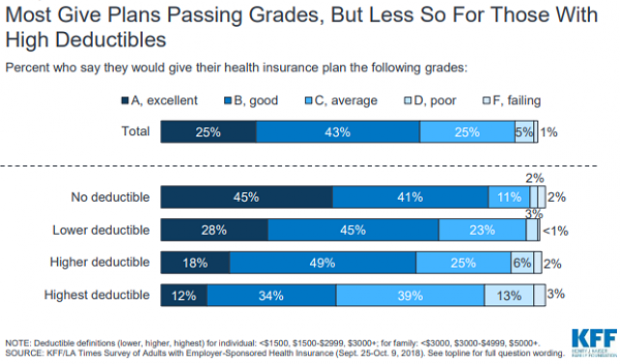
Chart of the Day: High Deductible Blues

The higher the deductible in your health insurance plan, the less happy you probably are with it. That’s according to a new report on employer-sponsored health insurance from the Kaiser Family Foundation and the Los Angeles Times.
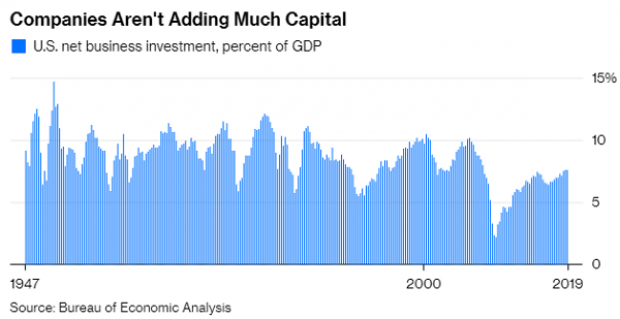
Chart of the Day: Tax Cuts and the Missing Capex Boom

Despite the Republican tax overhaul, businesses aren’t significantly increasing their capital expenditures. “The federal government will have to borrow an added $1 trillion through 2027 to pay for the corporate tax breaks,” says Bloomberg’s Mark Whitehouse. “So far, it’s hard to see what the country is getting in return.”
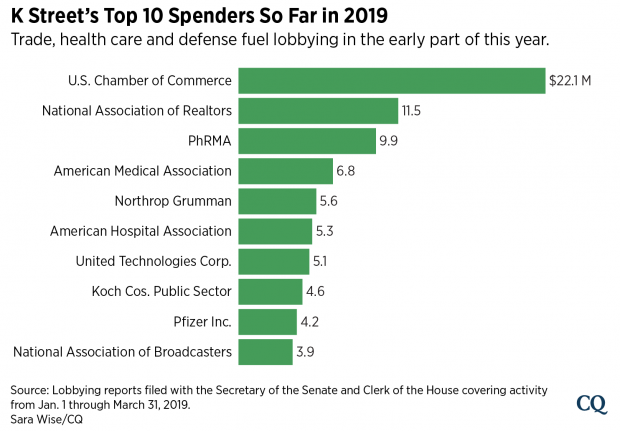
Chart of the Day: 2019’s Lobbying Leaders

Roll Call reports that trade, infrastructure and health care issues including prescription drug prices “dominated the lobbying agendas of some of the biggest spenders on K Street early this year.” Here’s Roll Call’s look at the top lobbying spenders so far this year:
Can You Fix Social Security? A New Tool Lets You Try

The Congressional Budget Office released an interactive tool Wednesday that shows how some widely discussed policy changes would affect the long-run financial health of the Social Security system.
“This interactive tool allows the user to explore seven policy options that could be used to improve the Social Security program’s finances and delay the trust funds’ exhaustion,” CBO said. “Four options would reduce benefits, and three options would increase payroll taxes. The tool allows for any combination of those options. It also lets the user change implementation dates and choose whether to show scheduled or payable benefits. … The tool also shows the impact of the options on different groups of people.”
Click here to view the interactive tool on the CBO website.
Why Prescription Drug Prices Keep Rising – and 3 Ways to Bring Them Down

Prescription drug prices have been rising at a blistering rate over the last few decades. Between 1980 and 2016, overall spending on prescription drugs rose from about $12 billion to roughly $330 billion, while its share of total health care spending doubled, from 5% to 10%.
Although lawmakers have shown renewed interest in addressing the problem, with pharmaceutical CEOs testifying before the Senate Finance Committee in February and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMS) scheduled to do so this week, no comprehensive plan to halt the relentless increase in prices has been proposed, let alone agreed upon.
Robin Feldman, a professor at the University of California Hastings College of Law, takes a look at the drug pricing system in a new book, “Drugs, Money and Secret Handshakes: The Unstoppable Growth of Prescription Drug Prices.” In a recent conversation with Bloomberg’s Joe Nocera, Feldman said that one of the key drivers of rising prices is the ongoing effort of pharmaceutical companies to maintain control of the market.
Fearing competition from lower-cost generics, drugmakers began over the last 10 or 15 years to focus on innovations “outside of the lab,” Feldman said. These innovations include paying PBMs to reduce competition from generics; creating complex systems of rebates to PBMs, hospitals and doctors to maintain high prices; and gaming the patent system to extend monopoly pricing power.
Feldman’s research on the dynamics of the drug market led her to formulate three general solutions for the problem of ever-rising prices:
1) Transparency: The current system thrives on secret deals between drug companies and middlemen. Transparency “lets competitors figure out how to compete and it lets regulators see where the bad behaviors occur,” Feldman says.
2) Patent limitations: Drugmakers have become experts at extending patents on existing drugs, often by making minor modifications in formulation, dosage or delivery. Feldman says that 78% of drugs getting new patents are actually old drugs gaining another round of protection, and thus another round of production and pricing exclusivity. A “one-and-done” patent system would eliminate this increasingly common strategy.
3) Simplification: Feldman says that “complexity breeds opportunity,” and warns that the U.S. “drug price system is so complex that the gaming opportunities are endless.” While “ruthless simplification” of regulatory rules and approval systems could help eliminate some of those opportunities, Feldman says that the U.S. doesn’t seem to be moving in this direction.
Read the full interview at Bloomberg News.