4 Reasons the Fed Won’t Raise Interest Rates in June
It is no surprise that the Fed didn’t take action on interest rates at the April Federal Open Market Committee meeting. The question of interest to the market is whether the Federal Reserve has revealed some clear signal in its statement about the timing of the future rate increase. Even though the Fed did not change its forward guidance on rate increases from the March statement, we can discern what the Fed has on its plate. Four aspects of the economy stand out:
Related: Bernanke Was Right—Interest Rates Aren’t Going Anywhere
- The latest GDP data show worse-than-expected growth at an annualized 0.2 percent during the first quarter of 2015, compared to 2.2 percent in the last quarter of 2014.
- The strong U.S. dollar has continued to weigh on exports. Net exports in the first quarter stayed unchanged (0.0 percent growth) year-over-year, compared with 18.6 percent growth in the fourth quarter of 2014.
- Inflation has continued to stay way below the central bank’s 2 percent target. The price index for personal consumption expenditure (PCE), the measure of inflation preferred by the Fed, showed a 0.3 percent year-over-year increase in the first quarter, much lower than the growth rate of 1.1 percent in the fourth quarter of last year. Core PCE inflation, which excludes volatile prices of food and energy, reached 1.3 percent, compared with 1.4 percent in the last quarter.
- The improvements in the labor market, the other mandate of the Federal Reserve besides inflation, also slowed. Only 126,000 employees were added to nonfarm payrolls in March, compared to 264,000 in February and 201,000 in January.
Related: Fed’s Downgrade of Economic Outlooks Signals Later Rates Lift-Off
In all, the U.S. economy is growing more slowly than anticipated with some headwinds that may last for a while, such as the strong dollar. Both measures of the Fed’s dual mandate, price stability and maximum employment, remain below the Fed’s target. Normally this would call for an accommodative monetary policy, postponing the rate increases until later in the year. Rather than starting rate increases at the June FOMC meeting, the liftoff in September instead is more likely.
This story originally appeared at the American Institute for Economic Research.
Stat of the Day: 0.2%

The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley tweets: “In order to raise enough revenue to start paying down the debt, Trump would need tariffs to be ~4% of GDP. They're currently 0.2%.”
Read Tankersley’s full breakdown of why tariffs won’t come close to eliminating the deficit or paying down the national debt here.
Number of the Day: 44%

The “short-term” health plans the Trump administration is promoting as low-cost alternatives to Obamacare aren’t bound by the Affordable Care Act’s requirement to spend a substantial majority of their premium revenues on medical care. UnitedHealth is the largest seller of short-term plans, according to Axios, which provided this interesting detail on just how profitable this type of insurance can be: “United’s short-term plans paid out 44% of their premium revenues last year for medical care. ACA plans have to pay out at least 80%.”
Number of the Day: 4,229

The Washington Post’s Fact Checkers on Wednesday updated their database of false and misleading claims made by President Trump: “As of day 558, he’s made 4,229 Trumpian claims — an increase of 978 in just two months.”
The tally, which works out to an average of almost 7.6 false or misleading claims a day, includes 432 problematics statements on trade and 336 claims on taxes. “Eighty-eight times, he has made the false assertion that he passed the biggest tax cut in U.S. history,” the Post says.
Number of the Day: $3 Billion

A new analysis by the Department of Health and Human Services finds that Medicare’s prescription drug program could have saved almost $3 billion in 2016 if pharmacies dispensed generic drugs instead of their brand-name counterparts, Axios reports. “But the savings total is inflated a bit, which HHS admits, because it doesn’t include rebates that brand-name drug makers give to [pharmacy benefit managers] and health plans — and PBMs are known to play games with generic drugs to juice their profits.”
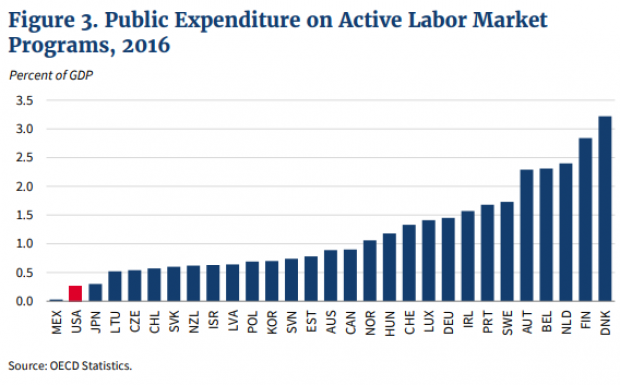
Chart of the Day: Public Spending on Job Programs

President Trump announced on Thursday the creation of a National Council for the American Worker, charged with developing “a national strategy for training and retraining workers for high-demand industries,” his daughter Ivanka wrote in The Wall Street Journal. A report from the president’s National Council on Economic Advisers earlier this week made it clear that the U.S. currently spends less public money on job programs than many other developed countries.